Esports isn’t just a trend—it’s a strategic opportunity to increase student engagement, build relevant career skills, and expand access to high-demand industries. For K–12 schools, esports offers a pathway to re-engage underserved students, support neurodiverse learners, and build inclusive programs that help students thrive both between and beyond the bell. Let’s explore how a well-designed esports ecosystem drives student success both in school and for their future—and how educators can implement these skills in school both between and beyond the bell.
The Difference Between Esports and Gaming
The esports ecosystem enables students to develop a wide range of skills across multiple career fields. I often say, “Esports is so much more than gaming”. While scholastic esports has grown in popularity over the past decade, many school, district, and county leaders do not fully understand its scope. Let me explain how esports differs from “just playing video games.”
When a gamer grabs an Xbox or PS5 controller and joins an online match, they’re dropped into a game with strangers. They don’t know the age, dynamic, or attitude of those playing.
Esports, however, offers a structured, intentional experience. Students on an esports club or competitive team know their teammates, develop sincere relationships with their teammates and coaches, and grow together, just like traditional team sports.
This sense of connection is especially powerful for students who have struggled to belong in other school settings due to many factors, including neurodivergence. Roughly 35% of all esports participants have neurodivergent classifications, and up to 60% of esports participants have never joined any other extracurricular activity. Esports creates a safe, engaging space where students develop essential skills much like traditional sports, including teamwork, collaboration, communication, sportsmanship, and strategic thinking, often through tools like video on demand (VOD) review.
When implemented with intention, esports becomes a modern learning environment where every student can find purpose, community, and a pathway to success.
From Gaming to Career Development
What does developing relationships on esports teams have to do with career skill development?
Esports is the gateway. A colleague once described it as the “chocolate on top of the broccoli.” Esports is an engaging and appealing layer that draws students into their schools and classrooms. Esports keeps students engaged before, during, and after the final bell. During these hours, students foster relationships, collaboratively explore the dynamics of computer processing, and begin to ask questions like How does this hardware work? Who built this game? What does it take to stream this event?
Their learning starts when students become curious about the design and development of the games they play, and when they learn how to maximize the setup of events, devices, and peripherals. The space and atmosphere esports provides gives students the ability to explore technical career pathways like:
- broadcasting, shout casting
- graphic design
- content creation and marketing
- entrepreneurship, business, finance
- mental and physical health in high-performance settings
Exploring the Full Esports Ecosystem
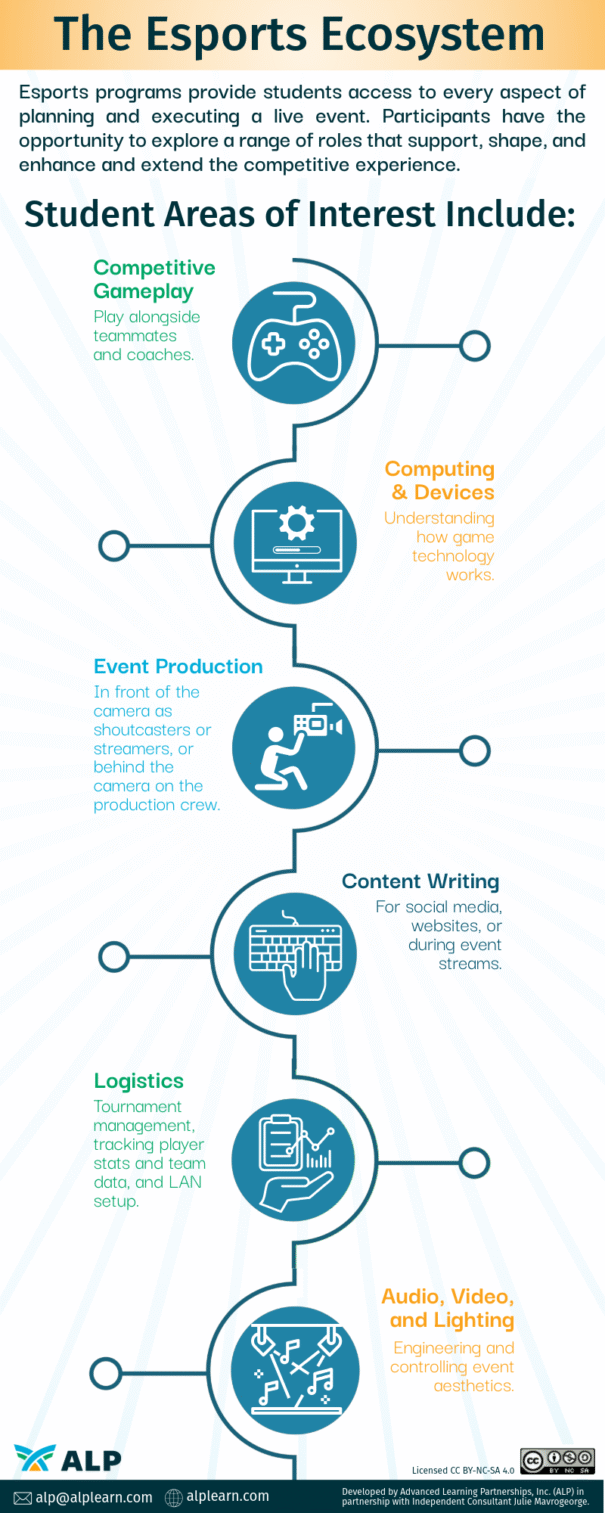
Esports is often compared to traditional sports. It is true they have many competitive similarities, but esports programs provide students access to every aspect of planning and executing a live event. Esports gives students access to the entire lifecycle of an esports event–from creating marketing materials and stream assets to planning event set up and logistics. This is the scope of the esports ecosystem. Esports participants have the opportunity to explore a range of roles that support, shape, and enhance and extend the competitive experience.
Some students enjoy competitive gameplay, while others may prefer to understand the inner workings of the devices on which the games are played. Some students enjoy being in front of the camera as a shoutcaster or streamer, while others prefer to be behind the camera as part of the production crew or writing the content shared on social media, websites, or during streams.
Students who enjoy logistics often have an affinity for tracking player stats and team data, as well as event and tournament management, including LAN setup. Beyond these roles, there are also audio, video, and lighting engineers who assist in ensuring that the event’s aesthetics are on par for the event. All of these are very lucrative careers that students can participate in learning while part of an esports club or competitive team.
In short, the esports ecosystem encompasses every facet of the season and tournament and the overall program. I often compare esports programs to the Super Bowl: every player on the field is backed by dozens of professionals who make the event possible, from the commentators to the production team, the referees to the coaches, athletic trainers, psychologists, doctors, and so many more. With 87% of students already playing video games, it is easy to see how esports serves as a powerful platform for teaching work-based learning, STEM skills, and career-connected competencies in a context that students find familiar and exciting.
Embedding Esports in Classrooms and CTE
Esports is easily integrated during school hours as an elective course, CTE (Career Technical Education) pathway, or embedded in existing CTE production, design, business, and marketing classes. No, students won’t just be “playing games.” They’ll be learning the high-value skills we’ve outlined.
In many states, these courses are embedded in CTE pathways. When clubs, courses, and competitions are aligned, esports becomes a fully sustainable program, not just an extracurricular activity.
The impact is clear. Students in robust esports programs have higher attendance, increased motivation, and find a deeper meaning in their education; therefore, they increase their GPAs, test scores, and attendance. Most importantly, students report a greater sense of purpose and clearer career direction.
Students can also earn scholarships to colleges not just for playing on esports teams but for managing teams, producing content, broadcasting, and shoutcasting, or leading tech support. Beyond the more obvious pathways are a host of additional potential career majors in esports law, finance, psychology, training and health sciences, and coaching. In addition, esports offers one of the few flexible internship models, allowing students to gain real-world experience through in-person, virtual, or hybrid placements. These opportunities often count toward both course credit and, potentially, industry certifications.
When implemented with intention, esports becomes a modern learning environment where every student can find purpose, community, and a pathway to success. Why not start a program? Esports is so much more than playing video games. It offers a bell-to-bell curriculum in addition to clubs and competitions. It encompasses a host of technical skill career development activities and the social/emotional skill development many employers and hiring managers indicate is lacking in today’s applicants.
As we have unveiled the truth of esports, we’ve discovered how effective it is in developing the whole student. From technical skills to social-emotional awareness, critical thinking, self-regulation, teamwork, collaboration, communication, conflict resolution, and quick decision-making. Esports brings all students together providing an experience that is both educational and engaging. And research shows that today’s most sought-after jobs require the very skills esports develops and employers seek.
Ready to bring esports to your district? ALP partners with districts to deliver strategic implementation, from infrastructure to curriculum to coaching. ALP also partners with technology providers like CDW, Lenovo, and Dell to leverage professional learning credits for consulting support. Talk to your technology provider for more information about professional learning credits, and reach out to ALP for more information on developing your esports clubs, curricula, and programs. Let’s build a future-ready program together.
Read more about why Every School Should Offer Esports.
Resources to learn more about esports in education
Esports Products, Solutions & Services | CDW
Esports in Education: Fostering Student Success – Intel
The Educational and Academic Benefits of Esports
What is esports? A systematic scoping review and concept analysis of esports – PMC
About the Author
Julie Mavrogeorge – Julie is the Founder and President of the California Esports Association, a Microsoft Innovative Education Expert, and serves as a Generation Esports, Minecraft Education, and Drone Legends Ambassador. She is an ALP consultant and has worked alongside Intel, CDW, British Esports, Spectrum Industries, LANFest, Minecraft Education, Generation Esports, and other partners to bring esports to districts including Los Angeles Unified, Fresno Unified, New York Public Schools, Atlanta Public Schools. Julie has presented on all facets of esports program development and implementation at The Future of Educational Technology Conference (FETC), Texas Computer Education Association (TCEA), International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE), DreamHack, and the National Association of Esports Coaches and Directors (NAECAD). She serves on the boards of NAECAD and Affinity Esports.
Connect with Julie on LinkedIn.

